As we step into 2024 and reflect on the previous year, it's astonishing to witness the tremendous changes in technology. Technologies that were once mere concepts are now commonplace, accessible to everyone. It almost feels like we're teetering on the edge of a robot takeover – or is that just our imagination running wild? Our world has become more cyber-centric than ever before. In terms of security, there has been a substantial escalation in cyber threats, with organizations reporting a staggering 48% increase in cyberattacks compared to previous years, according to ISACA.
It's a fascinating time to experience technology, where we celebrate remarkable advancements and, simultaneously, encounter the more ominous ways it can be exploited.
With the excitement of 2023 now behind us, we're ready to unveil what lies ahead in the cyber world for 2024. Strap in, and let's explore what this year has in store for us:
|
Trend 3: Zero Trust Architecture
|
1. AI and Machine Learning Integration:
No surprise here but first on the list is the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) into cybersecurity. Leveraging this technology is rapidly gaining momentum as we move into 2024. These technologies are not just buzzwords; they are becoming central to enhancing the capabilities of cybersecurity systems.
As noted by TechTarget, AI and ML are transforming the way cybersecurity systems operate by providing more sophisticated and real-time responses to threats. The integration of these technologies enables systems to learn from past incidents, enhancing their ability to predict and prevent future attacks. TechTarget quotes experts saying, "AI and ML are revolutionizing cybersecurity, providing the ability to quickly analyze millions of events and identify a multitude of potential threats."
AI and ML can adapt and evolve to counteract the continuously changing tactics of cyber attackers. This adaptability is key in a landscape where cyber threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated.
Beyond just threat detection and mitigation, AI and ML are also expected to contribute significantly to operational efficiencies within cybersecurity. By automating routine tasks and analyzing large datasets quickly, these technologies free up human resources to focus on more complex and strategic activities.
2. Quantum Computing
Okay, what the heck does that even mean?
Your regular computer uses a simple system to solve problems; either 'yes' (1) or a 'no' (0). This is called binary code.
Now, quantum computing can use the 'yes' or 'no' answers, but also all kinds of answers in between, all at the same time. In quantum computing, it uses 'qubits' instead of regular bits. Unlike a regular bit that can be only 0 or 1, a qubit can be sort of 0, sort of 1, or both at the same time, thanks to what’s called superposition.
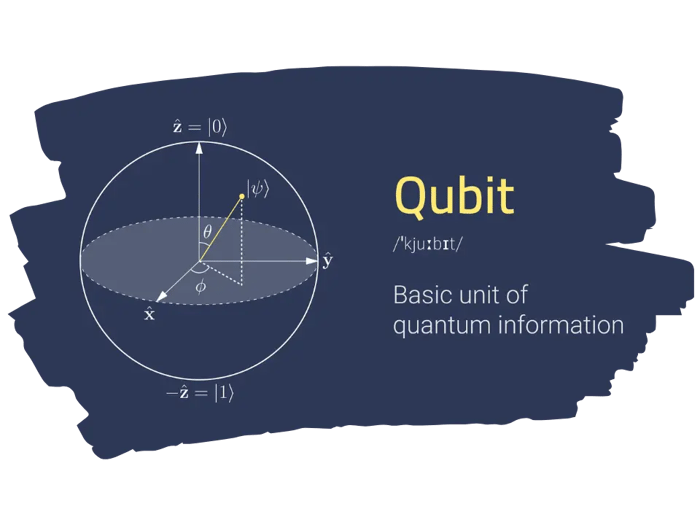 Visualization of a Qubit. Photo Credit: Devopedia
Visualization of a Qubit. Photo Credit: Devopedia
That’s pretty technical but the exciting thing about quantum computing is that it can handle a huge number of calculations all at once. It's like being able to check every single possible answer to a problem at the same time, rather than one by one. This makes quantum computers super powerful for certain types of problems.
But, there's a catch in terms of cybersecurity. Just as quantum computers can solve complex problems quickly, they can also break some types of digital locks (encryption) that we currently use to keep data safe. So, while they're great for making new, super-strong security methods, they also challenge our existing security measures, which means we need to come up with new ways to protect data in the era of quantum computing.
3. Zero Trust Architecture
Here’s another more technical term that we’re going to breakdown.
Zero Trust Architecture is like having a strict intuitive security guard at every door of a building, constantly checking everyone's ID. In traditional security models, once you're inside a network (like being inside a building), you're generally trusted and can move around freely. But in Zero Trust Architecture, it's like the security guard never stops checking your ID, no matter where you are in the building.
Here's how it works:
Never Trust, Always Verify: Zero Trust means exactly that. The system doesn't automatically trust anyone, even if they are already inside the network. Just like a security guard who double-checks your ID at every door, the system continuously verifies who's trying to access data or resources.
Minimizing Risks: By always verifying, Zero Trust Architecture reduces the chance of unauthorized access. It's like having a lock on every door, not just the front gate, making it harder for someone who shouldn't be there to get in.
Verification Methods: This might include passwords and biometrics (fingerprints or facial recognition), or tokens (a special code sent to your phone). It's all about making sure the person accessing the information is really who they say they are.
Role-Based Access: In a Zero Trust system, you only get access to what you need for your job. Similar to a hospital where doctors, nurses, and administrative staff have access to different areas and information based on their roles. This limits exposure to sensitive data.
Protects Against Inside and Outside Threats: Zero Trust isn't just about stopping strangers from getting in; it's also about keeping an eye on people inside the network. This is important because sometimes security threats come from inside an organization.
As more work moves online and cyber threats grow more sophisticated, Zero Trust Architecture is becoming a go-to strategy for many organizations. For more information around implementing Zero Trust, review our resources section on the topic: https://blog.primesecured.com/it/tag/zero-trust
Our Blog
Subscribe to the Prime Secured blog to receive the latest updates.
4. The Evolution of Ransomware & Phishing Attacks
Ransomware
Ransomware, a type of malicious software that locks users out of their systems or data and demands payment for its release, is expected to evolve and become even more sophisticated in the near future.
One of the advanced techniques that is increasingly being used by cybercriminals is known as "double extortion."
Here’s how it works:
Initial Attack: First, the attackers encrypt the victim's data, making it inaccessible.
Double Threat: In addition to demanding a ransom for decrypting the data, attackers also threaten to leak sensitive information they have stolen from the victim's network if their demands are not met.
Increased Leverage: This double threat gives attackers extra leverage. Even if victims can restore their data from backups, the threat of public exposure of sensitive data adds significant pressure to pay the ransom.
Sophisticated Targeting: Cybercriminals are also becoming more selective and strategic in targeting their victims. They often focus on organizations that are most likely to pay large sums, such as those in critical industries or with sensitive data.
Use of Advanced Technologies: Ransomware attackers are leveraging more advanced technologies, including AI and ML, to identify vulnerabilities, optimize their attack strategies, and evade detection.
Rising Costs: With these advanced techniques, the cost of ransomware attacks is increasing, not only in terms of the ransom payments but also due to the associated downtime, reputational damage, and loss of consumer trust.
The evolution of ransomware highlights the need for robust cybersecurity measures, regular data backups, employee training on phishing and other attack vectors, and a solid incident response plan.

Phishing Attacks
Phishing, a form of cyberattack where criminals trick individuals into revealing sensitive information or downloading malware, is evolving in sophistication, making it a more intimidating threat than ever before. Here's exactly how it’s evolving.
More Convincing Emails and Messages: Modern phishing attempts are harder to spot. Attackers are using AI and advanced software to craft emails that closely mimic the style and tone of legitimate messages from trusted sources. They often include personal details scraped from social media or other public platforms to make the emails seem more credible.
Targeting Specific Individuals or Companies (Spear Phishing): Rather than sending mass, generic emails, phishers are now targeting specific individuals or companies with personalized messages. This approach, known as spear phishing, increases the likelihood of someone falling for the scam.
Use of Multi-stage Attacks: Instead of just one deceptive email, phishers are using multi-stage attacks. The first message might seem harmless but is designed to build trust. Subsequent messages will then seek to extract sensitive information or deliver malware.
Exploiting Current Events: Phishers often take advantage of current events, crises, or trends to make their attacks more relevant and convincing. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, there were numerous phishing campaigns exploiting people's need for information or assistance related to the virus.
Bypassing Traditional Security Measures: As phishing tactics become more refined, they are increasingly able to bypass traditional security measures like spam filters and antivirus software. This is partly because these techniques often rely on deception and manipulation, rather than just technical means like malware, to trick victims.
Emphasizing the Need for Robust Authentication Systems: To combat the rise in sophisticated phishing attacks, there's a growing need for more robust authentication systems. Multi-factor authentication (MFA), where users must provide two or more verification factors to gain access to a system or account, is becoming essential. MFA makes it much harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access, even if they have tricked a user into revealing one set of credentials.
5. Mobile Security Focus
Mobile devices in both our personal and professional lives are driving a significant shift towards enhanced mobile security solutions. This shift is a response to the growing recognition of the unique security challenges posed by our mobile devices. Here are some things to consider:
Unique Challenges for Mobile Devices: Our phones serve as mini offices, banks, and entertainment centers, containing everything from personal photos to crucial work emails. Unlike laptops or desktops, they face a unique challenge due to their constant presence, increasing the risk of loss or theft. Additionally, our frequent use of public Wi-Fi without a second thought adds to the vulnerability of our phones, exposing them to potential security risks.
Rise of Mobile Malware and Attacks: As the use of mobile devices has increased, so has the frequency of attacks targeting these devices. This includes malware, phishing attacks specifically tailored to mobile interfaces, and targeting mobile operating systems and apps.
Need for Specialized Security Solutions: Traditional cybersecurity solutions are often not fully suited to mobile devices. As a result, there's a growing need for security solutions specifically designed for mobile. These solutions need to be lightweight and efficient, as mobile devices have limited processing power and battery life compared to traditional computers.
Secure Mobile Access and Authentication: With more employees accessing company resources remotely via mobile devices, secure mobile access solutions are essential. This includes the use of VPNs, encrypted communications, and robust authentication protocols to ensure that only authorized users can access sensitive data and systems.
Staying Smart about Security: A big part of keeping our phones safe is just being smart about how we use them. This means keeping an eye out for fishy emails and apps.
Privacy Matters Too: Mobile security isn't just about preventing unauthorized access or data breaches; it's also about protecting user privacy. This includes managing app permissions and ensuring that personal data isn't being unnecessarily collected or shared.
As our phones become more and more central to our lives, keeping them secure is critical which is why this is a rising trend in 2024.
6. Cloud Security & Cloud Jacking
Cloud security and the issue of cloud jacking are on the rise as our reliance on cloud services grows. Cloud jacking is a type of cyberattack where hackers exploit vulnerabilities in cloud computing environments to gain unauthorized access. Let's break this down a bit:
Growing Dependence on the Cloud: Nowadays, a lot of our data and applications are stored on cloud services. This includes everything from personal photos and emails, to business-critical applications and databases. The cloud offers flexibility, scalability, and cost savings, but it also presents new security challenges.
What is Cloud Jacking? Cloud jacking is a type of cyberattack where attackers exploit vulnerabilities in cloud computing services to gain unauthorized access. This can involve compromising cloud environments, such as servers or storage systems, hosted by third-party providers.
Cloud environments are complex and often involve multiple services and integrations. Hackers look for weak points, like misconfigured settings or outdated software, to break in. Once inside, attackers can do serious damage. They might lock up data with ransomware, demanding payment to release it, or they might quietly steal sensitive information for other malicious purposes.
The Need for Robust Cloud Security: To protect against cloud jacking, it's essential to have strong security measures in place. This includes regular security audits, proper configuration of cloud settings, and using encryption to protect data. Continuous monitoring of cloud environments can help quickly identify and respond to any suspicious activity. It's about being proactive rather than reactive.
Concerned about what you're up against for 2024?
We know that might have been a lot to process, and many of the trends we covered consist of new ways cybercriminals are trying to prevail. However, we hope this was a beneficial resource. If you are concerned about where your organization stands against cyberattacks, give Prime Secured a call. We are an excellent first step to assess your current IT environment.
We'd also love to hear from you! What are some trends in cybersecurity you've noticed? Or maybe you've got some thoughts on what we've discussed. Drop your comments below and let's keep this important conversation going.

